Abstract
Background:
Mutations in chromatin modifying genes (CMGs) including KMT2D, CREBBP, EZH2, and EP300 have been inferred as early events in follicular lymphoma (FL) by truncal status in mature tumors and persistence between diagnosis and relapse. We previously reported frequent detection of CREBBP lysine acetyltransferase (KAT) domain mutations in pre-diagnostic blood and tissue specimens from individuals later developing FL (Schroers-Martin et al, ASH Annual Meeting 2017). However, the limited availability of paired tumor biopsies has precluded confirmation of concordance between precursor lesions and subsequent clinical malignancy.
Methods:
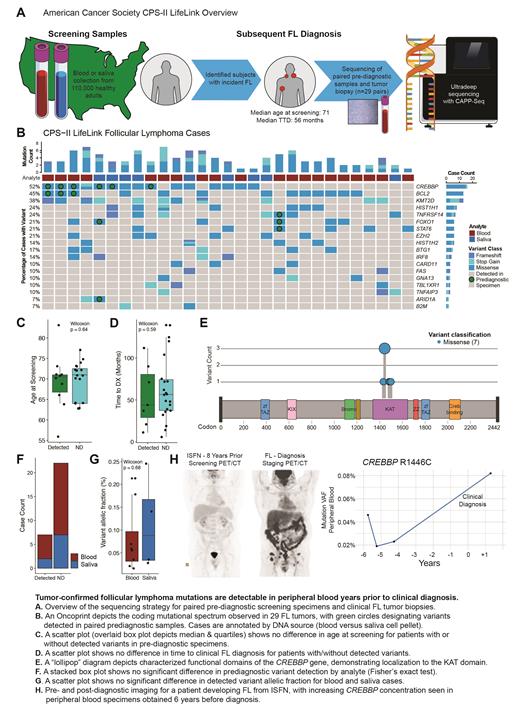
The American Cancer Society (ACS) Cancer Prevention Study-II (CPS-II) LifeLink cohort collected screening blood or saliva samples from over 100,000 cancer-free American participants between 1998 and 2002. To evaluate detection of tumor-confirmed variants in pre-diagnostic specimens, we identified 29 FL patients with available FFPE tumor biopsy and screening sample (Fig A). The median age at screening was 71 years (range 56-83) with a median time to FL diagnosis of 56 months (TTD, range 6-139).
Tumor biopsies were sequenced utilizing hybrid capture sequencing for commonly mutated lymphoma genes. DNA extracted from pre-diagnostic blood or saliva cell pellet specimens was sequenced utilizing error-corrected CAPP-Seq (Newman et al Nat Biotech 2016) to a median depth of 5204x. We sequenced to similar depths peripheral blood DNA from control cohorts of individuals with detectable t(14;18) but no subsequent lymphoma diagnosis (n=14) and healthy individuals without detectable t(14;18) by PCR (n=20).
Results:
Coding mutations were identified from all tumors with a mutational distribution similar to prior FL sequencing studies. Tumor-derived variants were detected in 7 of 29 paired pre-diagnostic specimens (24%) at a median TTD of 44 months (range 11-112 months, Fig B). The statistical significance of detection was assessed using a previously described approach based on Monte Carlo sampling (Newman et al Nat Biotech 2016) and the error distribution of affected loci in control cohorts.
While an outlier case contained concordant TNFRSF14, FOXO1, and STAT6 mutations 90 months pre-diagnosis at an elevated allelic fraction (AF) of 1.8%, the mean AF of other detected precursor variants was 0.091%. Individuals with detected variants were not older (Fig C) nor significantly closer to clinical diagnosis (Fig D). The most frequently detected lesions were CREBBP (6/15 cases, 40%) and BCL2 (3/13, 23%) with one case demonstrating a fuller mutational profile including FOXO1 and ARID1A at 44 months before diagnosis. All detected precursor CREBBP variants localized to the KAT domain, reflecting prior observations in pre-diagnostic samples without confirmatory biopsy (Fig E). Of note, saliva cell pellets may contain 30% or more hematopoietic DNA (Kaur et al Chimerism 2012) and we detected tumor-confirmed variants in both saliva and blood screening specimens (Fig F) with no significant difference in AF (Fig G).
In an illustrative independent case with available imaging, a patient undergoing radical prostatectomy was found to have involvement of a pelvic lymph node with in situ follicular neoplasia (ISFN). Staging PET/CT showed no evidence of FL (Fig H) and he was followed expectantly for 4 years without emergent disease. Eight years after surgery he presented with inguinal swelling and bilateral FDG-avid adenopathy on PET/CT. Excisional biopsy confirmed low grade FL and sequencing for M7-FLIPI revealed a CREBBP KAT domain variant. Retrospective sequencing of serial peripheral blood specimens from his initial surveillance showed detectable CREBBP R1446C at the earliest collected time point (AF range 0.019-0.046%) rising to AF 0.082% after clinical diagnosis.
Conclusions:
Precursor FL mutations are detectable in peripheral blood and saliva years prior to clinical diagnosis with a spectrum of variants enriched in CREBBP and BCL2 and concordant with subsequent FL tumors. Such lesions may assist in stratifying individuals at elevated risk of clinical malignancy, including after identification of pathologic precursors such as ISFN.
Kurtz: Foresight Diagnostics: Consultancy, Current holder of stock options in a privately-held company; Roche: Consultancy; Genentech: Consultancy. Khodadoust: Alexion, AstraZeneca Rare Disease: Other: Study investigator; CRISPR Therapeutics, Nutcracker Therapeutics: Research Funding; Myeloid Therapeutics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Diehn: Roche: Consultancy; AstraZeneca: Consultancy; RefleXion: Consultancy; BioNTech: Consultancy; Varian Medical Systems: Research Funding; Illumina: Research Funding; CiberMed: Current holder of stock options in a privately-held company, Patents & Royalties; Foresight Diagnostics: Current holder of individual stocks in a privately-held company, Current holder of stock options in a privately-held company. Roulland: BMS: Research Funding. Alizadeh: Bristol Myers Squibb: Research Funding; Gilead: Consultancy; CAPP Medical: Current holder of individual stocks in a privately-held company, Current holder of stock options in a privately-held company; Celgene: Consultancy, Research Funding; Roche: Consultancy, Honoraria; Janssen Oncology: Honoraria; Foresight Diagnostics: Consultancy, Current holder of individual stocks in a privately-held company, Current holder of stock options in a privately-held company; Cibermed: Consultancy, Current holder of individual stocks in a privately-held company, Current holder of stock options in a privately-held company; Forty Seven: Current holder of individual stocks in a privately-held company, Current holder of stock options in a privately-held company.